The Snow Graphs - Historical Series are intended to represent, starting from October and until the end of June, the snow depth on the ground (Hs) measured manually in 12 points of the Aosta Valley, i.e. the fixed snow fields, in which the Modello 1 AINEVA are daily performed between 7.00 and 9.00.
The measurement snow fields considered are the following:
|
Station Code
|
Altitude
|
Municipality
|
Location
|
Start of the time series
|
|
03VG
|
1658 m
|
Valgrisenche
|
Loc. Capoluogo
|
1972
|
|
04RH
|
1725 m
|
Rhêmes-Notre-Dame
|
Loc. Capoluogo
|
1996
|
|
05DY
|
1530 m
|
Valsavarenche
|
Loc. Dégioz
|
1996
|
|
06CE
|
1680 m
|
Cogne
|
Loc. Valnontey - Giardino Paradisia
|
1996
|
|
07CH
|
1420 m
|
Champorcher
|
Loc. Capoluogo
|
1996
|
|
4GAB
|
2380 m
|
Gressoney-La-Trinité
|
Diga Gabiet
|
1928
|
|
3GOJ
|
2540 m
|
Valtournenche
|
Diga Goillet
|
1996
|
|
1CGN
|
2150 m
|
Valtournenche
|
Diga Cignanaz
|
1996
|
|
2PLM
|
1970 m
|
Bionaz
|
Diga Place-Moulin
|
1963
|
|
13SR
|
1750 m
|
Saint-Rhémy-en-Bosses
|
Loc. Ronc
|
1996
|
|
CF01
|
1025 m
|
Pré-Saint-Didier
|
Stazione forestale
|
2007
|
|
CF08
|
690 m
|
Aosta
|
Stazione forestale
|
2005
|
In particular, each graph shows (Figure 1):
- in light blue the snow depth data (Hs) relating to the current season;
- in blue the minimum values ??of snow depth over the entire available historical series. The longest time series (4GAB) starts from 1928, while the shortest (CF01) starts from 2007;
- in red the maximum values ??of snow depth over the entire available historical series. The longest time series (4GAB) starts from 1928, while the shortest (CF01) starts from 2007;
- in grey the normal range of Hs data is shown, considering the period from 1996 until the season preceding the current one (the current season is not taken into account). In particular, the grey line indicates the daily mean value of Hs (averaged with a moving average, over the period from October 1996 until July of the season preceding the current one, except for CF01 and CF08 as the data are available only after 1996). The grey area instead indicates the value of the standard deviation.
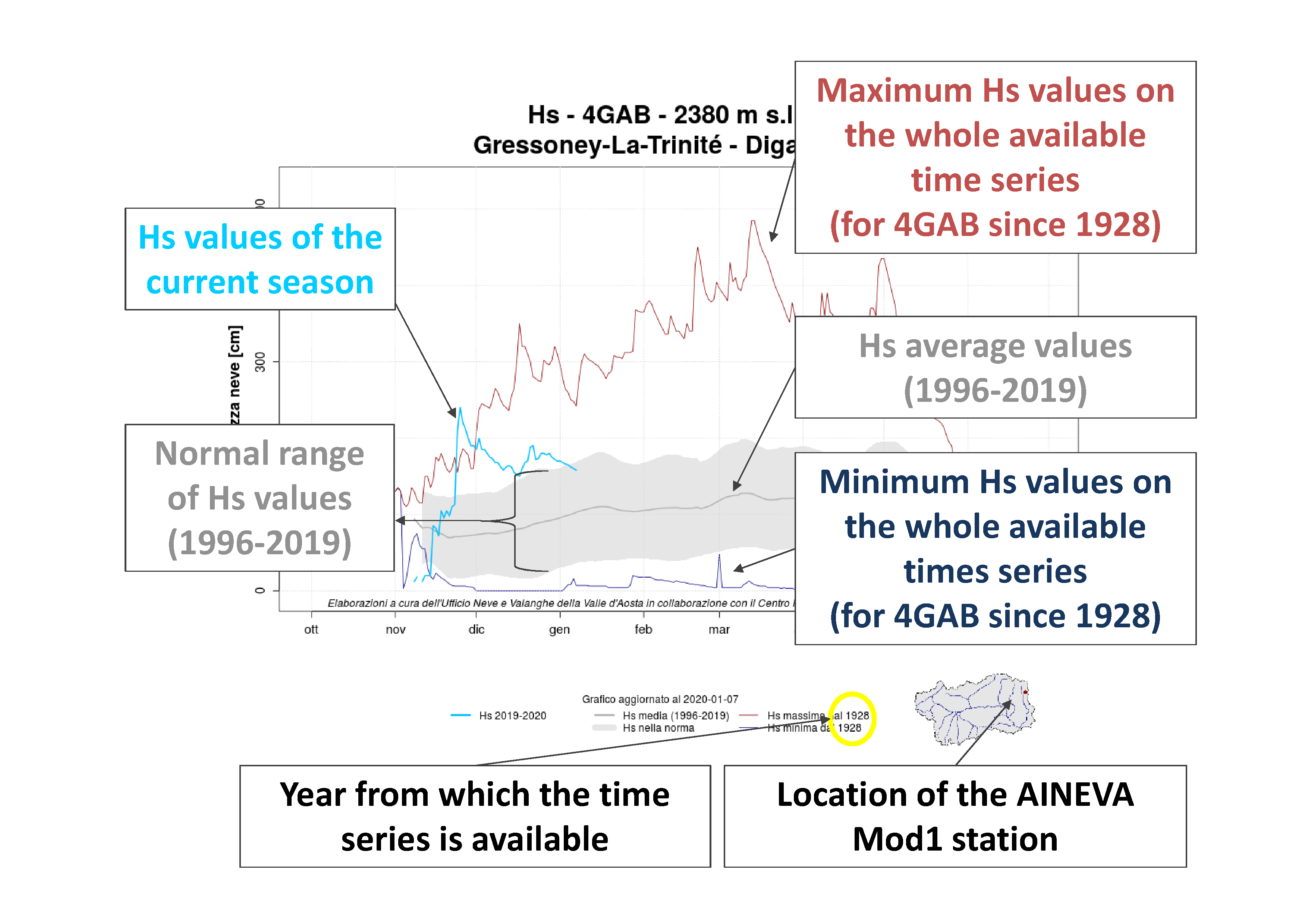
Figure 1: example of a Snow Graph - Historical Series with relative explanations.
Figures 2 and 3 show some examples about how to read a graph.
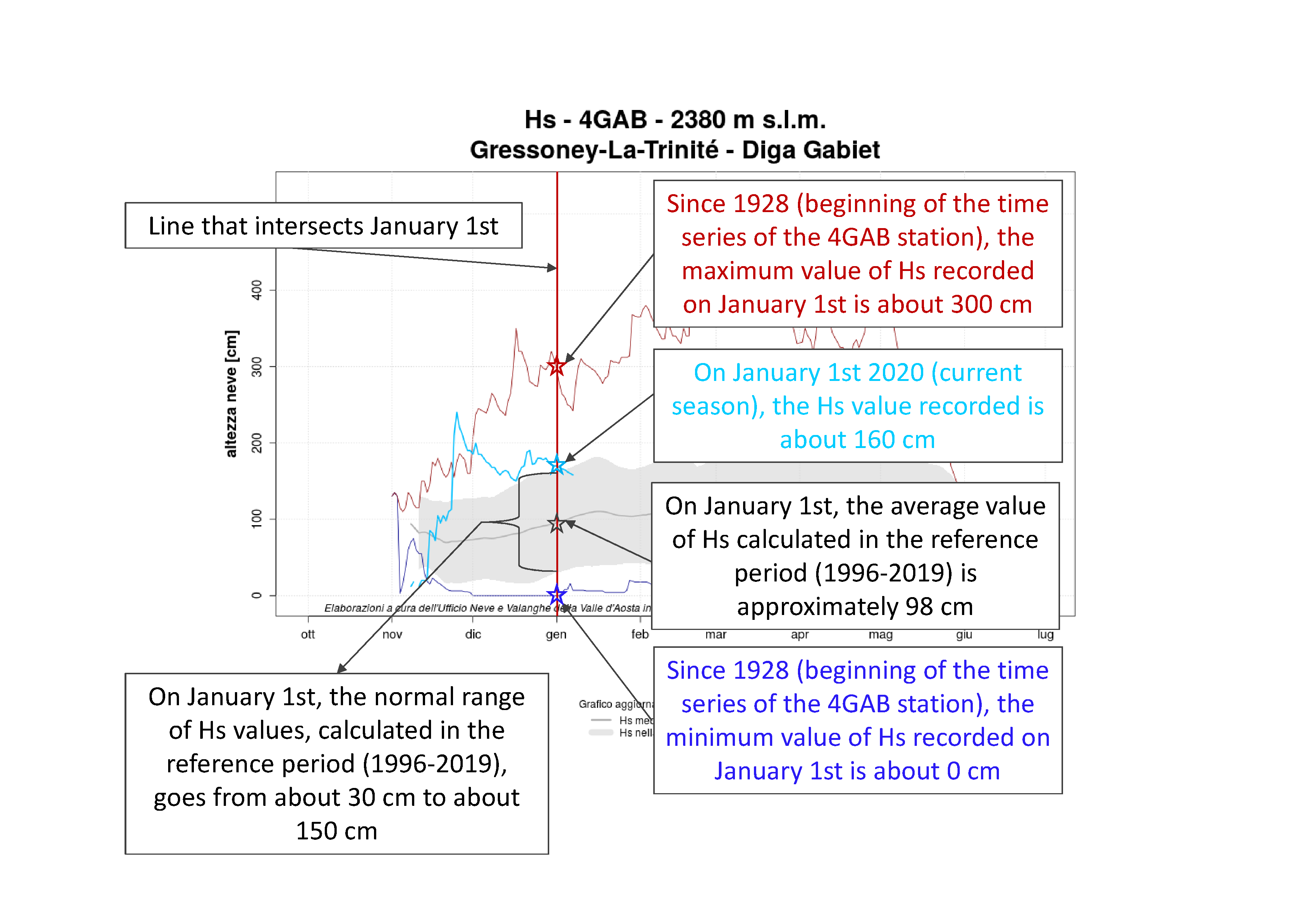
Figure 2: some information that can be obtained from a Snow Graph - Historical Series, by analysing a specific day, in the example January 1st.
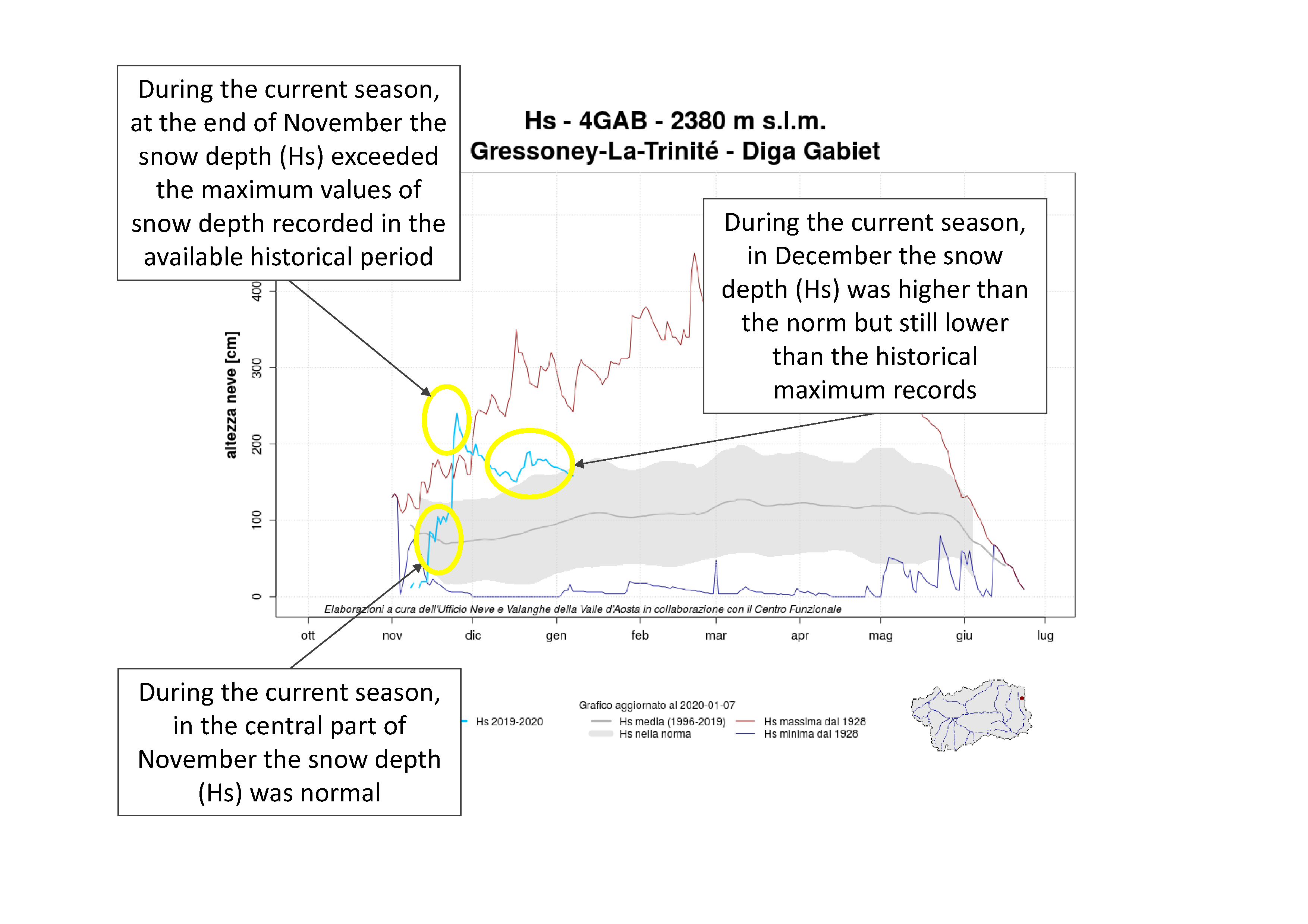
Figure 3: some information that can be obtained analysing a Snow Graph - Historical Series